Our Universe is made of 69% dark energy, 27% dark matter, 1% normal matter.
What is plasma?
Plasma is also called the “fourth state of matter”. Solid is heated to become a liquid, liquid is heated to become a gas.
Upon further heating, the gas is ionized into a plasma. Since plasma usually exists only in a vacuum, we need to pump the air out of a vacuum chamber in the laboratory.
The Definition of Plasma
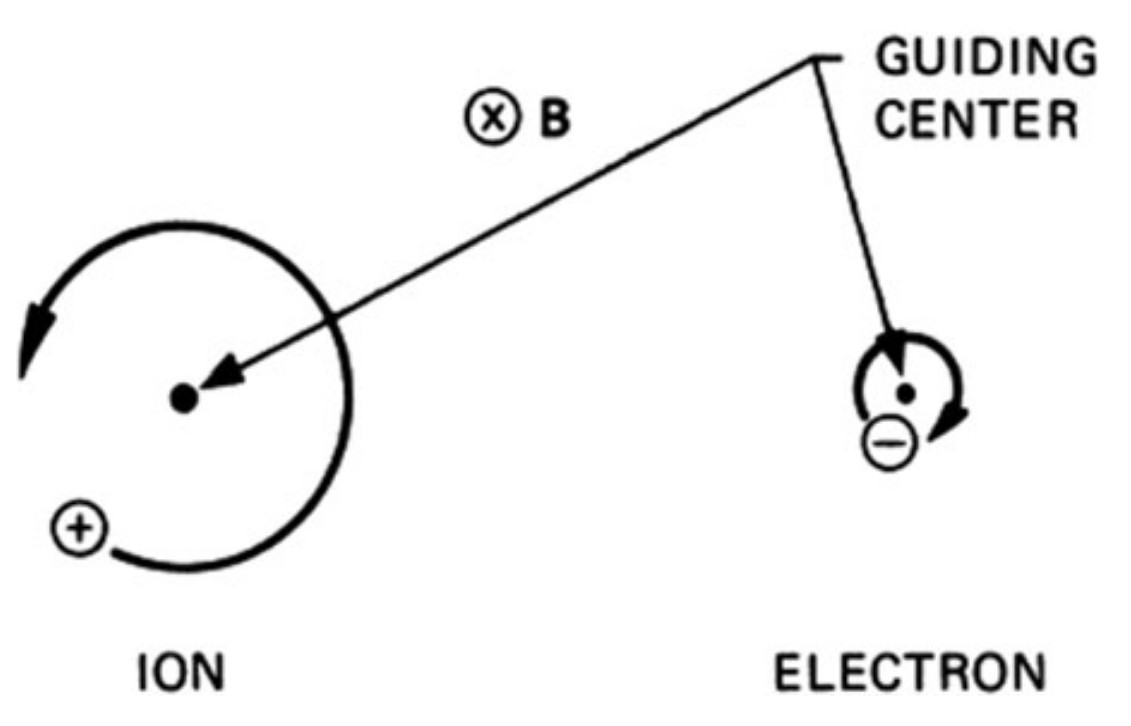
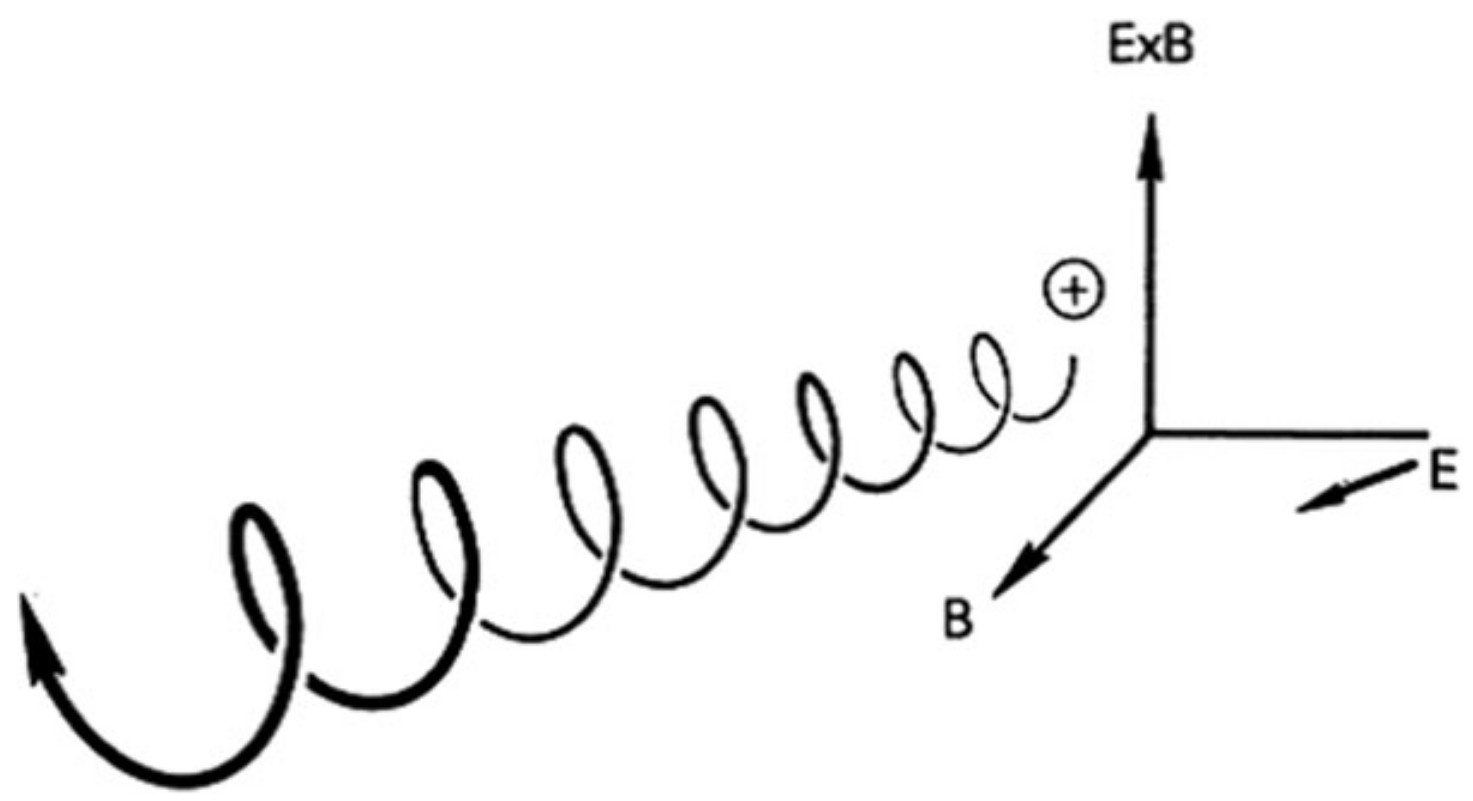
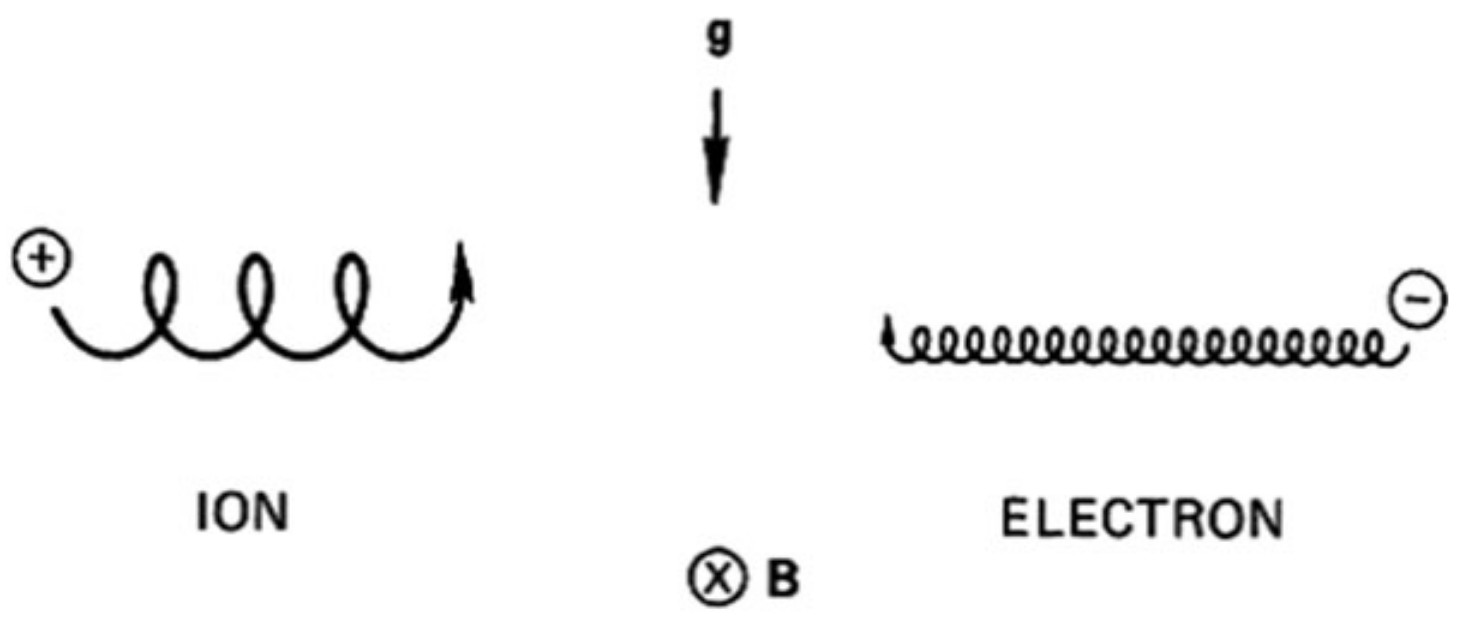
A plasma is a quasineutral gas of charged and neutral particles which exhibits collective behavior.
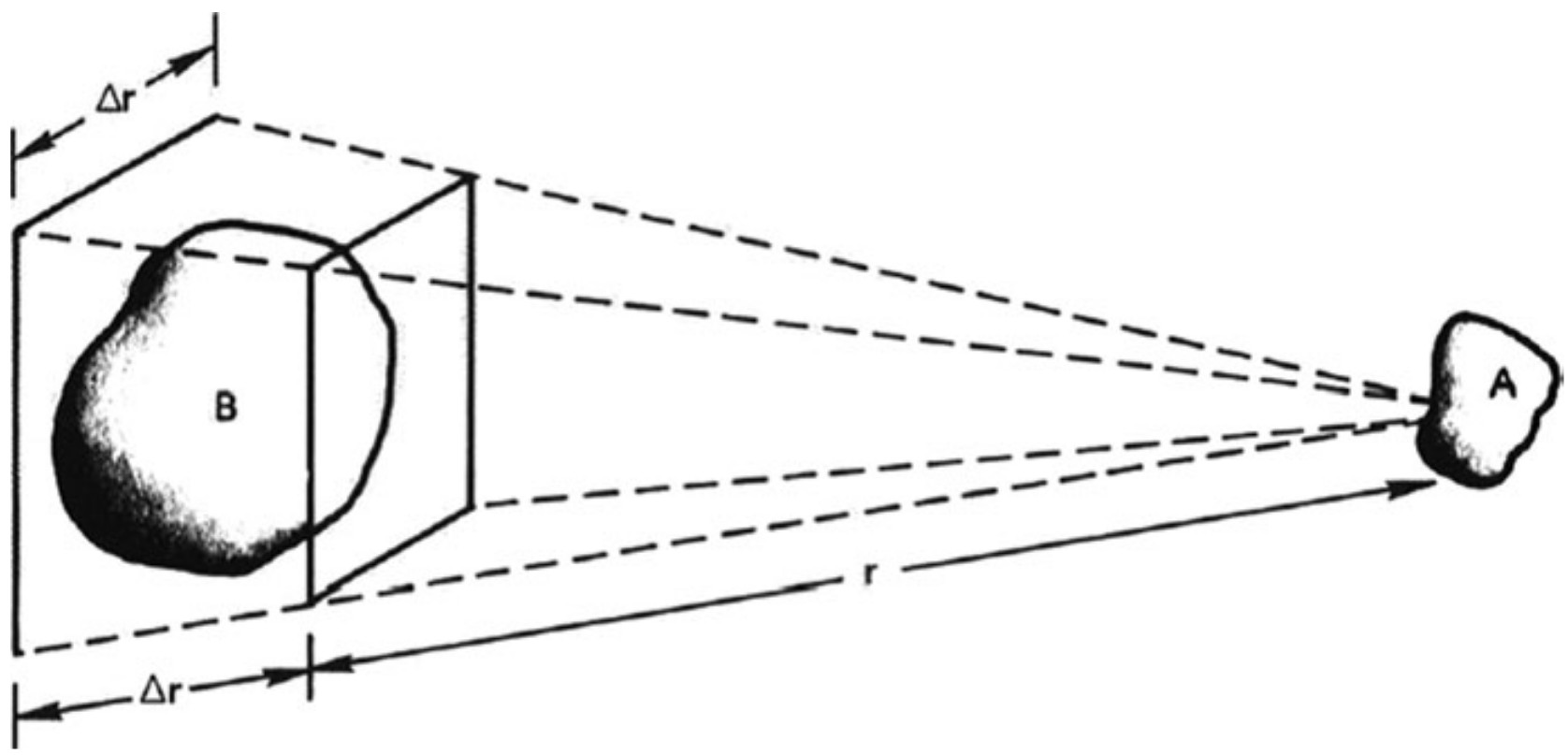
- The Coulomb force between A and B diminishes as .
- However, for a given solid angle($\Delta$r/r = constant), the volume of plasma in B that can affect A increases as .
The Saha Equation
Physical meaning
When temperature is raising, the whole value is increasing exponentially with .
The higher value of , the lower recombination rate of ionized atoms.
The Maxwellian Distribution
The one-dimensional Maxwellian distribution
Boltzmann’s constant K
The particles density n
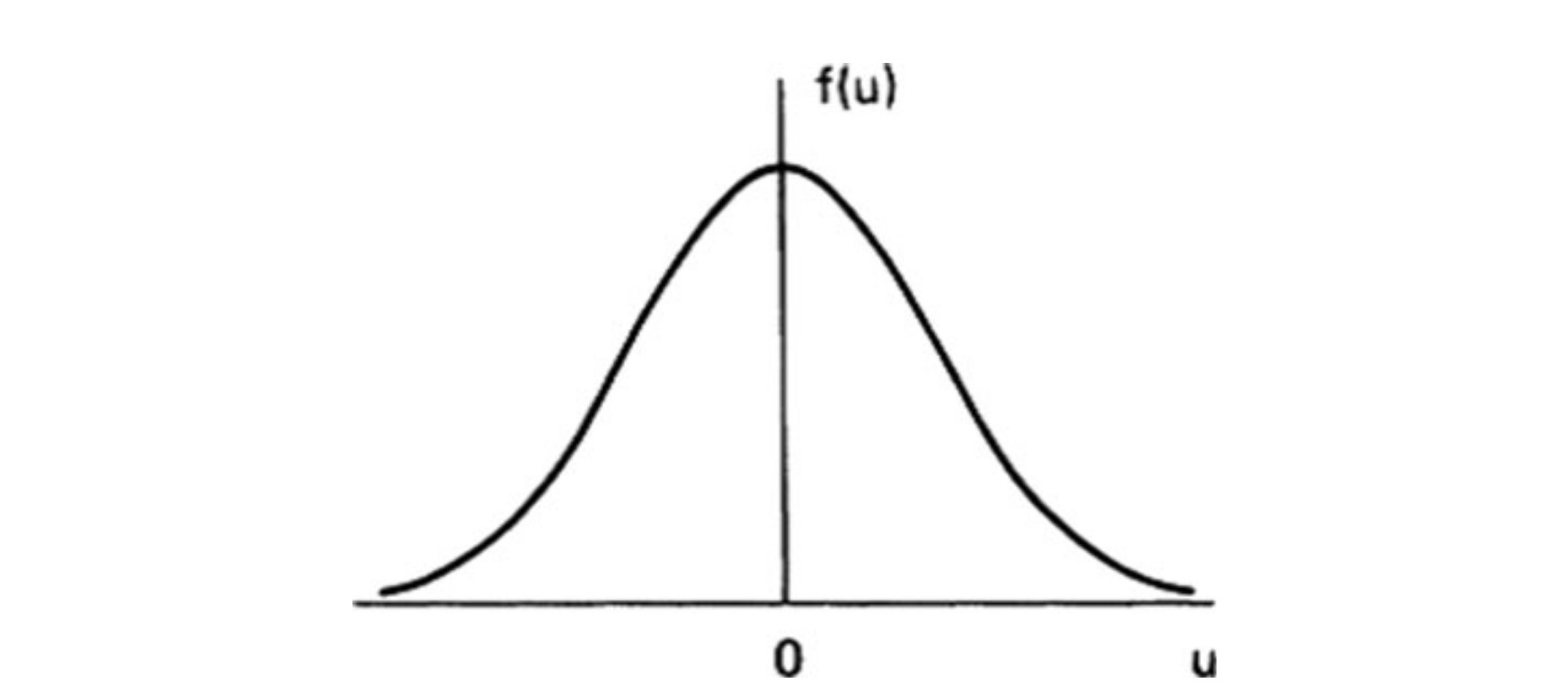
The average kinetic energy is $\frac{1}{2}KT$
The three-dimensional Maxwellian distribution
Reference Book
Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion by Francis F. Chen